Biological Diversity How Do We Explain Differences Among Organisms
The variety of life on Earth its biological diversity is commonly referred to as biodiversity. In a biological sense classification is the systematic grouping of organisms based on structural or functional similarities or evolutionary history.

Biodiversity Why Is Biodiversity So Important
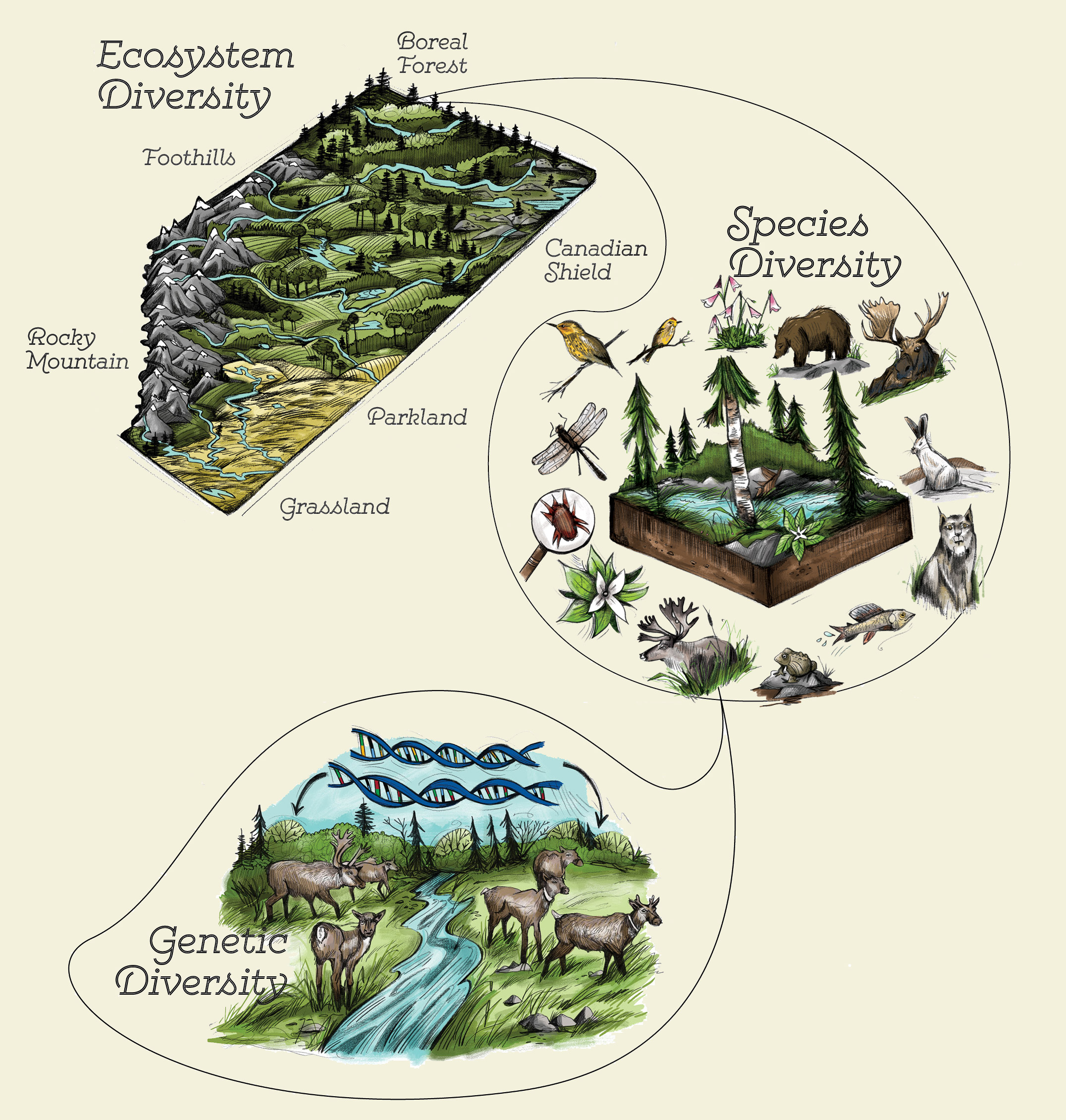
Species diversity is defined as the number of different species present in an ecosystem and relative abundance of each of those species Diversity is greatest when all the species present are equally abundant in the area.

. Person who studies the natural history or natural development of organisms and the environment. The theory of evolution is one of the fundamental keystones of modern biological theory. The 1992 United Nations Earth Summit defined biological diversity as the variability among living organisms from all sources including inter alia terrestrial marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part.
One commonly used threshold is that two populations with sharp boundaries are considered to be different races if 25 or more of the genetic variability that they collectively share is found as between population differences. Evolutionary biologists study the evolution of living things in everything from the microscopic world to ecosystems. Taxonomy the classification of organisms into a system that indicates natural relationships.
Genetic variations can arise from gene variants also called mutations or from a normal process in which genetic material is rearranged as a cell is getting ready to divide known as genetic recombination. This includes diversity within species between species and ecosystems. Biological diversity is reflected in the range of species found in local and global environments and by subtle variations in.
Order sensitivity or response to the environment reproduction adaptation growth and development regulationhomeostasis energy processing and evolution. An organism that evolves characteristics fit for the environment will have greater reproductive success subject to the forces of natural selection. Proteobacteria are Gram-negative bacteria and share a common rRNA sequence.
All living organisms share several key characteristics or functions. The source of this diversity is evolution the process of gradual change during which new species arise from older species. When viewed together these eight characteristics serve to define life.
An individual living thing. It has a focus on life science with a secondary focus on Earth and space science. Evolution theory in biology postulating that the various types of plants animals and other living things on Earth have their origin in other preexisting types and that the distinguishable differences are due to modifications in successive generations.
Examples include pathogenic bacteria such as Vibrio cholerae that causes cholera and those that are residents of the body like Escherichia coli E. Quercus rubra--red oak tree. There are two constituents of species diversity.
Is part of Smithsonian Science for the Classroom a brand new curriculum series by the Smithsonian Science Education Center. Their offspring are able to breed. Difference or variety of units of inheritance genes in a species.
Ecology is the study of interaction of organisms with one another and with the environment. Tigers and lions are separate species. A process of establishing defining and ranking taxa within hierarchical series of groups.
What Explains Similarities and Differences Between Organisms. Area that contains a significant level of biodiversity and is threatened with destruction. It is aligned to a group of grade 3 standards.
The number of species of plants animals and microorganisms the enormous diversity of genes in these species the different ecosystems on the planet such as deserts rainforests and coral reefs are all part of a biologically diverse Earth. Biodiversity Biodiversity is the variability among living organisms from all sources including terrestrial marine and other aquatic ecosystems. They interbreed in nature.
Evolution and Diversity - Opportunities in Biology - NCBI Bookshelf. Evolution of the horse. Up to 24 cash back explain biological diversity in terms of the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection by examining the changes in and diversification of life since it first appeared on the Earth analyse how an accumulation of microevolutionary changes can drive evolutionary changes and speciation over time for example.
The fact that biology as a science has such a broad scope has to do with the tremendous diversity of life on earth. Up to 24 cash back 8MHR Biological Diversity Organisms are often grouped together as a species if. This includes diversity within species between species and of ecosystems.
They are not known to breed together in the wild. Number of different species present in an ecosystem. The domain is divided into five groups based on their genetic differences.
A race or subspecies requires a degree of genetic differentiation that is well above the level of genetic differences that exist among local populations. A group of populations of similar organisms that reproduce among themselves but do not naturally reproduce with any other kinds of organisms eg Haliaeetus leucocephalus--bald eagle. Tigers and lions have been bred together in zoos but their offspring are infertile.
C In such a relationship organisms are parasitic or mutually benefited from each other or mutually dependent on another organism. A group of individuals belonging to one species living in an area. Relative to other species we are genetically all very similar.
Evolution and diversity result from the interactions between organisms and their environments and the consequences of these interactions over long periods of time. The diversity of life on Earth is a result of mutations or random changes in hereditary material over time. Up to 24 cash back Overview.
A Organisms that have a peculiar water-driven tube system that they use for moving around. Now think about the diversity index you calculated in the diversity and succession labs. Name the phylum to which the following organisms belong.
Organisms continually adapt to their environments and the diversity of environments that exists promotes a diversity of organisms adapted to them. Genetic variations that alter gene activity or protein function can introduce different traits in an organism. These mutations allow the possibility for organisms to adapt to a changing environment.
The three main aspects of biodiversity include genetic diversity species diversity and ecosystem diversity. However in contrast in terms of our phenotype meaning how we look externally.
The Diversity Of Life Biology For Majors I

The Maintenance Of Species Diversity Learn Science At Scitable

Comments
Post a Comment